| |
|
 |
|
|
| |
|
 |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
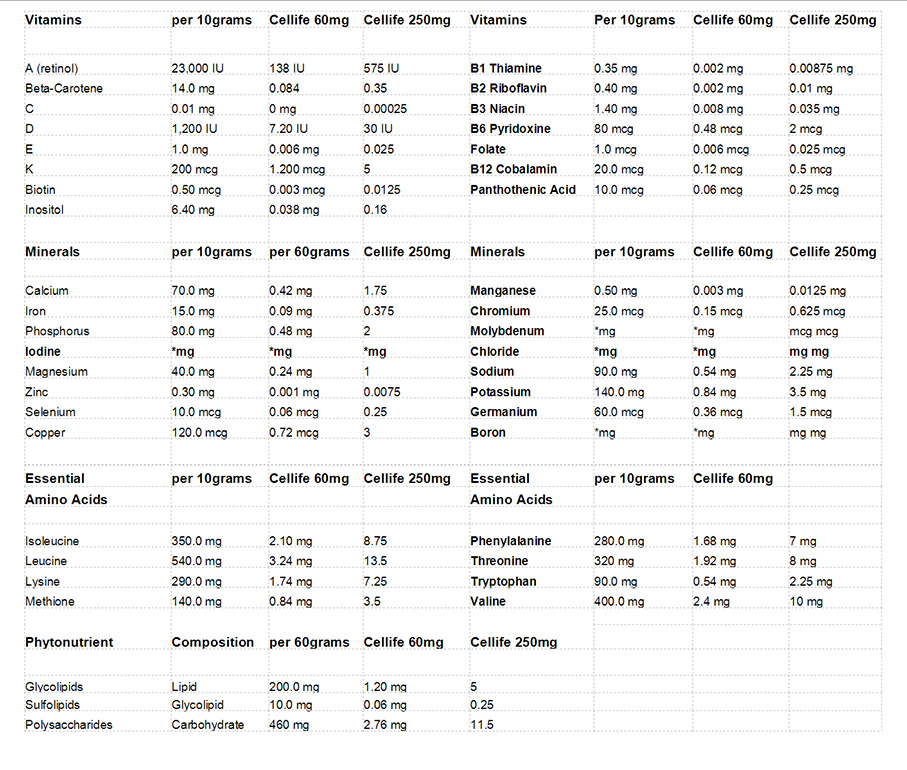
Cellife is all organic, 100% natural
and with 95% bio-availability.
Nutritional Requirements
Many nutrients can be synthesized in the
body. Those that can’t be synthesized in the
body-called essential nutrients-must be
consumed in the diet. They include amino
acids (in proteins), certain fatty acids (in
fats and oils), minerals, and vitamins. Nine
of the 20 amino acids in proteins are
essential nutrients. If essential nutrients
are not supplied in the quantities required,
nutritional deficiency disorders may result.
To determine whether a person is getting
enough nutrients, a doctor asks about eating
habits and diet, performs a physical
examination to asses the composition (the
amount of fat and muscle0 and functioning of
the body, and orders laboratory tests to
measure the nutrient content of blood and
tissues.
Generally, nutrients are divided into two
classes: macronutrients, which include
proteins, fats, carbohydrates, and some
minerals, are required daily in large
quantities They constitute the bulk of the
diet and supply the energy and building
blocks needed for growth, maintenance, and
activity. Micronutrients are required in
small quantities-milligrams (one thousandth
of a gram) to micrograms (one millionth of a
gram). They include vitamins and trace
minerals that catalyze the utilization of
macronutrients.
The other useful components of food aren't
digested or metabolized to any appreciable
extent. These components include some fibers,
such as cellulose, pectins, and gums.
Authorities recommended that 20 grams of
fiber be consumed daily to improve movement
in the gastrointestinal tract, moderate the
changes in blood sugar and cholesterol that
occur after meals, and increase the
elimination of cancer-causing substances
produced by the bacteria in the large
intestine. Food additives such as
preservatives, emulsifiers, anti-oxidants,
and stabilizers improve the production,
processing storage, and packaging of foods.
Substances such as spices, flavors, odors,
phytochemicals (non-nutrients in plants,
which have biologic activity in animals0,
and many other natural products improve the
appearance, taste, and stability of the
food. Food in the daily diet contains as
many as 100,000 substances, of which only
300 are nutrients and 45 are essential
nutrients.
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are a vital part of a
healthy diet. If a person eats a variety of
foods, the likelihood of developing a
deficiency of these nutrients is very small.
However, people who follow restrictive diets
may not get enough of a particular vitamin
or mineral. For example, strict vegetarians
may become deficient in vitamin B12, which
is available only in animal products. On the
other hand, consuming large amounts (megadoses)
of vitamin and mineral supplements, without
medical supervision, may have harmful
(toxic) effects.
Vitamins
Vitamins are essential micronutrients,
required by the body in small amounts. They
are either fat soluble - A,D,E, and K - or
water soluble - the B vitamins and vitamin
C. The B vitamins include vitamins B1, B2,
and B6, panthothenic acid, niacin, biotin,
folic acid (folate), and vitamin B12. The
recommended daily allowance (RDA) - the
amount an average person needs each day to
remain healthy - has been determined for
each vitamin. A person who consumes too
little or too much of certain vitamins may
develop a nutritional disorder.
When taken in daily doses that are more than
10 times the recommended daily allowance,
vitamins A and D are toxic, but vitamins E
and K (phylloquinone) are not. Niacin,
vitamin B6, and vitamin C are toxic when
taken in high doses, but the other
water-soluble vitamins are not.
Only two fat-soluble vitamins (A and E) are
stored in the body to any extent. Vitamins D
and K are stored in tiny amounts. Relative
to requirements, vitamins C is stored in the
smallest amounts, and vitamin B12 is stored
in the largest amounts, requiring about 7
years to exhaust the body’s reserves of 2 or
3 milligrams.
Minerals
Some minerals - sodium, chloride, potassium,
calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium - are
considered macronutrients because they’re
needed by the body in relatively large
quantities; they’re called macrominerals.
Other minerals are micronutrients because
they’re needed by the body in small or trace
minerals. They include iron, zinc, copper,
manganese, molybdenum, selenium, iodine, and
fluoride. Deficiencies of minerals, except
iron and iodine, are uncommon. Excesses of
some minerals cause toxicity.
Source: The Merck Manual of
Medical Information
Caution: Always consult
your Physician before taking any medicine or
supplement.
|
|
|
| |
|
Vitamins
|
Action
|
Highlight
|
Vitamin A
|
Anti-oxidant
Anti-carcinogenic
|
Dietary
intake of
beta-beta-carotene
and vitamin
A may reduce
the risk of
chronic
illnesses
(i.e. heart
disease2 and
cancer1,3).
|
Vitamin B
complex
(B1,2,3,5,6,7,12,
Folic Acid,
PABA,
inositol,
choline)
|
Nerve
stabilizer
Brain cell
function
GIT health
function
|
Vitamin B
complex
gives relief
of
moodiness,
restlessness,
irritability,
insomnia and
fatigue6.
Brings
health of
the skin,
bones, hair
and muscles.
Improves
liver health
and the
mucosal
membrane of
mouth.
|
B3
|
Cholesterol
regulator
Energy
releaser
|
Vitamin B3
(niacin)
stimulates
the release
of HGH7.
Works with
B1 and B2 to
release
energy from
carbohydrates8.
|
B12
|
Nerve
stabilizer
Anti-dementia
Anti-anemia
Homocysteine
regulator
|
Needed in
the
production
of
mood-affecting
substance
SAMe
(S-adenol-Syl-L-methionine9).
Lowers risk
of heart
attack,
stroke,
osteoporosis
and
Alzheimer’s
diseases by
lowering the
homocysteine
level10.
|
Folic Acid
|
Anti-nueral
tube defects
Neuroprotective
anti-depressant
Anti-atherogenic
Anti-carcinogenic
|
Badly needed
to women
planning to
get pregnant
to avoid
neural tube
defect like
meningocoele,
spina bifida
etc.11, 12.
Important in
the nucleic
acid
metabolism,
control in
the
homocysteine
formation to
methionine13
|
Vitamin C
|
Anti-scurvy
Anti-oxidant
Detoxifier
|
A biological
reducing
agent for
the
prevention
of
degenerative
diseases4,5
needed for
the
synthesis of
collagen and
connective
tissues5.
The
detoxifier
of the
interstitial
region4.
|
Vitamin D
|
Anti-rickets
Anti-osteomalacia
|
Exposure to
sunlight
with Vitamin
D decreases
risk of
colon,
breast and
prostate
cancer14. An
important
vitamin in
the
treatment of
psoriasis15
|
Vitamin E
|
Anti-oxidant
Cell
membrane
stabilizer
|
Prevents the
oxidation of
LDL and
formation of
cholesterol
plaques16.
|
|
|
|
| |
|
MINERALS AND
TRACE
ELEMENTS
|
|
CHROMIUM
|
Highly
required in
sugar
metabolism.
It makes the
insulin
sensitive to
glucose. A
big help to
diabetes
type II.
Lowers LDL,
triglycerides,
incidence of
hardening of
blood
vessels.
|
SELENIUM
|
Needed in
the
formation of
connective
tissues,
synergistic
with
Vitamins E
and C to
fight
against
cancer. An
Anti-oxidant,
anti-inflammatory
and reduces
incidence of
cardiovascular
diseases.
|
ZINC
|
An important
trace
element that
is badly
needed in
the
formation of
hormones and
enzymes.
|
VANADIUM
|
Very
important in
lowering the
blood
pressure by
reducing the
production
of
cholesterol.
Reduces
insulin
requirement
in Diabetic
Type I and
promotes
storage of
glucose in
muscles in
the form of
glycogen.
|
IODINE,
BORON,
MOLYBDENUM
|
Are in
negligible
amounts
although
enough to
give
physiological
effects
inside the
body.
|
PHYTONUTRIENTS:
|
Nutrients
from plants
(and or
vegetables)
|
PHYTONUTRIENT
BETA-CAROTENE
(Vit. A
precursor)
|
Action:
Anti-carcinogenic
Beta
carotene is
one of the
most
effective
substances
to
counteract
those free
radicals
that alter
cells
causing
cancer13,
14. Studies
at the
Harvard
University
School of
Dental
Medicine
found a
reduction in
mouth cancer
when
beta-carotene
extracts,
obtained
from
Arthrospira
platensis
are
consumed15.
Arthrospira
platensis
extract
induces the
tumor
necrosis
factor in
macrophages,
suggesting a
possible
tumor
destruction
mechanism.
|
PHYTONUTRIENT
CHLOROPHYLL
|
Action:
Detoxifier,
Anti-anemic
The “green
blood”
easily
converted to
hemoglobin
and a
substance to
detoxify the
liver and
the
gastrointestinal
tract2.
|
PHYTONUTRIENT
PHYTOSTEROL
|
Action:
Anti-cholesterol
Inhibits the
absorption
of
cholesterol
from the
intestine,
very
effective in
lowering
cholesterol
(Low Density
Lipoprotein)
and
triglycerides1,2.
|
PHYTONUTRIENT
PHYCOCYANIN
|
Action:
Immune
System
Enhancer,
Anti-arthritic,
Liver
protective
Phycocyanin
acts
directly to
the stem
cells of the
bone marrow
to produce
strong
natural
killer
cells, T and
B cells24. A
potent
analgesic
and
anti-inflammatory25.
Hepato-protective
and promotes
the
regeneration
of the liver
cells26. An
anti-oxidant
to
neutralize
the
ill-effects
of
electromagnetic
wave2.
|
PHYTONUTRIENT
POLYSACCHARIDES
|
Action: Cell
detoxifier,
Anti-cancer
Arthrospira
platensis
has
chemo-protective
and
radio-protective
capability,
and maybe a
potential
good adjunct
to cancer
therapy20.
|
CALCIUM
SPIRULAN
|
Action:
Anti-viral
Calcium-Spirulan
(Ca-Sp),
made up of
rhamnose,
ribose,
mannose,
fructose,
galactose,
xylose,
glucose,
glucuronic
acid,
galacturonic
acid, and
calcium
sulfate
obtained
from
Arthrospira
showed
activity
against HIV,
Herpes
Simplex
virus, Human
Cytomegalovirus,
Influenza A
virus, Mumps
virus and
Measles
virus17, 18.
Current
investigation
in this
field is
searching
for extracts
that inhibit
the AIDS
virus
replication
and allows
these
patients to
improve
their
health19.
|
PHYTONUTRIENT
GAMMA
LINOLENIC
ACID
|
Action: A
colostrums
like EFA,
called the
“gatekeeper”
of health
and beauty,
Anti-diabetic,
Anti-osteoporosis,
Anti-hypertensive,
Anti-arthritis
In
Diabetics,
assist nerve
function and
help prevent
peripheral
neuropathy3
Eye
Diseases,
GLA may be
beneficial
in dry-eye
conditions
such as
Sjogren’s
syndrome.
Osteoporosis,
studies have
shown that
supplements
of FLA and
EPA together
help
maintain or
increase
bone mass.
EFA may also
enhance
calcium
absorption,
increase
calcium
deposits in
bones,
diminish
calcium loss
in urine,
improve bone
strength,
and enhance
bone growth,
all of which
may
contribute
to improved
bone mass
and
strength4.
Rheumatoid
Arthritis,
some
preliminary
information
indicates
that GLA,
may diminish
joint pain,
swelling and
morning
stiffness.
GLA may also
lessen the
use of pain
medications5.
Attention
Deficit/
Hyperactivity
Disorder
(ADHD)
researches
to date
suggested an
improvement
in symptoms
and
behaviors
related to
ADHD from
omega-3
fatty acids.
Results of
studies
supplying
omega-6
fatty acids
in the form
of GLA from
EPO or other
sources to
children
with ADHD,
however,
have been
mixed and,
therefore,
not
conclusive.
In the
meantime,
ensuring a
healthier
balance of
omega-3 to
omega-6
fatty acids
in the diet
seems
worthwhile
for those
with this
behavioral
condition7,8.
Cancer, GLA
has shown
some
benefits for
breast
cancer in
certain
studies as
well as
colon, and
other types
of cancer9.
High Blood
Pressure and
Heart
Disease,
studies
suggest that
GLA, either
alone or in
combination
with two
important
omega-3
fatty acids,
EPA and DHA,
may lower
the blood
pressure of
hypertensive
individuals
and that the
EFA and GLA
helped to
prevent the
development
of heart
disease in
animals as
well as in
humans10.
Premenstrual
Syndrome
(PMS) and
Menopausal
Syndrome,
the use of
GLA
supplements
may help
most of the
breast
tenderness,
feelings of
depression
as well as
irritability
and swelling
and bloating
from fluid
retention11.
GLA lowers
low-density
lipoprotein,
being
170-fold
more
effective
than LA
(Cohen,
1997)12.
|
PHYTONUTRIENT
SULFOGLYCOLIPIDS |
Action:
Anti-viral
Inhibit the
multiplication
of herpes
simplex
virus23.
|
PHYTONUTRIENT
TRITERPENOIDS
|
Action:
Anti-cancer,
Anti-hypertensive,
Anti-diabetic,
relaxant and
sleep
inducer
Arthrospira
triterpenoids
increases
the
production
of
interferon
that will
act to
prevent the
multiplication
of cancer
cells21.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
For
inquiries,
Please contact
(63) 571-1458 |
|
|
| |
|
or visit
www.pharmaceiajimenez.com |
|
|
| |
|
or email us
at
info@pharmacieajimenez.com
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|


